Heart is one of the vital organs in humans. The heart itself never stops pumping blood in the body throughout the super long blood vessels that are 100 000 kilometres in length. Throughout a human’s lifetime, the heart never stops pumping blood and never gives up to keep us going with life. Hence, you should be taking care of your heart health seriously so that your heart can keep doing what it should until the end of your life. Having a healthy heart can provide you a healthier life and the ability to do many things in life with ease. Unfortunately, not everyone will have a healthy functional heart throughout their life and be diagnosed with a variety of heart diseases.
What is heart failure? It is a condition characterised by the impairment of the heart function or heart structures that leads to the heart unable to pump blood as demanded by the body blood circulation system. Heart failure (HF) around the world is around 64.34 million cases. HF not only increases risk for disability but also death. Risk for a person to have HF increases as a person gets older. The risk for HF in men doubles with each 10-year age increase after the age 65 whereas in women it is triple. Risk for HF not only increases by age. Risk is heightened when a person has metabolic risk factors from the sedentary lifestyle such as obesity and diabetes.
Have you ever thought about heart failure as a normal consequence of getting old? It is certainly not a normal thing. As a matter of fact, heart failure is typically the aftermath of the long-standing high blood pressure. However, there is no denying that the ageing process may have caused the heart structures to deteriorate and this itself leads to susceptibility of heart failure.
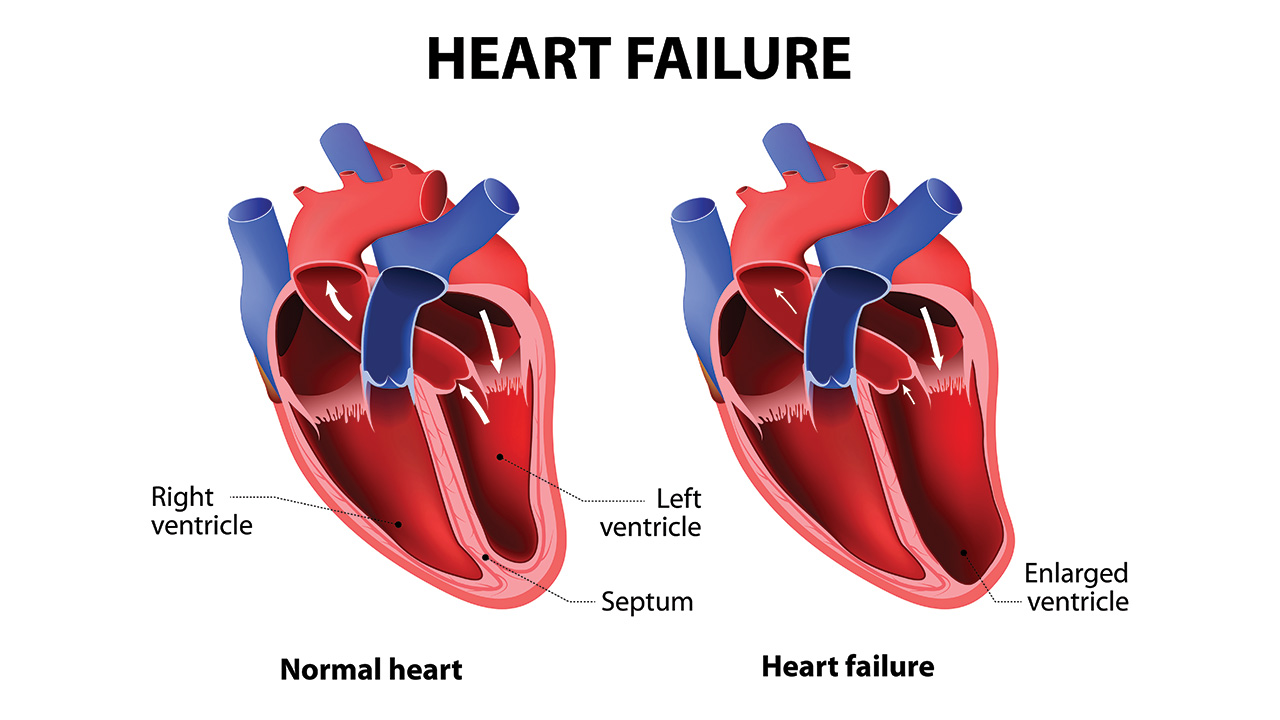
HF can occur to one or both sides of the heart. In right-sided heart failure, the heart is too weak to pump enough blood to the lungs for oxygen. In left-sided heart failure, the heart is too weak to pump enough blood to the whole body. Left-sided heart failure is more common than right-sided heart failure. HF does not mean the heart stops beating but because it works less efficiently than it should, it leads to the organs not receiving enough blood and precipitating into serious problems.
There are two types of heart failure. The first one is systolic heart failure that occurs when the heart muscle is not able to contract with enough force to pump blood in the blood circulation system. The second one is diastolic heart failure that occurs when the heart contracts normally but the ventricles of the heart are not properly relaxed or have become stiff. This makes less blood able to enter the heart during the normal blood filling phase in between heartbeats. To determine if heart failure is systolic or diastolic dysfunction. Echocardiogram test will be done to evaluate the heart pump function.
HF is caused by many causes but the most common and main cause is usually due to coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD is a disease caused by the plaque build-up made of cholesterol deposits in the wall of the arteries that affect the blood supply to the heart. Other causes of HF include cardiomyopathy, inflammation of the heart muscle such as endocarditis, congenital heart defects, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) and heart valve diseases. Conditions that overwork the heart such as those with high blood pressure, kidney disease, diabetes, obesity and bad lifestyles such as alcohol, drugs and emotional distress.
The heart chambers initially respond to blood flow by stretching to hold more blood or become thickened to the extent of stiffness. Temporarily, this does help to keep the blood flow smoothly but as time goes by, it leads to the heart muscle weakening and ultimately unable to pump efficiently. Kidney will then respond to this condition by retaining the fluid and salt. This then led to fluid build-up in the many organs, commonly visible in legs, feet and lungs, to become congested. Hence, congestive heart failure is named after the congested event.
Heart failure symptoms can range from mild to severe. It can be constant or come and go. Symptoms depend on which side of the heart is affected. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue even after taking rest, swelling of the lower legs or abdomen, temporary rapid weight gain, difficulty to sleep when lying flat, swelling in the veins of the neck, persistent coughing and nausea. Some even urinate more than usual and have chest pain when it is caused by heart attack. Symptoms may also include kidney or liver damages and malnutrition.
In essence, heart failure is one of the heart diseases that contributes to high mortality rate. It is important for people to understand their risk factors with the hope that they can get early medical intervention. Heart failure is not a normal ending for the elderly.
Also read – Dengue Prevention.